American vs European Airplanes: Key Differences
- aviatorpro_6714
When you board an airplane, you probably don’t think much about where it was made. However, the differences between American and European airplanes are quite significant and worth exploring. Whether you’re a commercial pilot, an aviation enthusiast, or simply a curious traveler, understanding these distinctions can offer fascinating insights into the aviation industry.
The history of aviation in the United States and Europe has followed different trajectories, leading to distinct approaches in aircraft design and manufacturing. In the early days of aviation, both regions were pioneers, but their paths diverged as the industry matured.
The American Approach
In the United States, the emphasis has traditionally been on creating robust and versatile airplanes. This can be traced back to the country’s vast geography and the need for aircraft to cover long distances efficiently. American manufacturers such as Boeing and Lockheed Martin focused on building larger airplanes that could handle diverse conditions.
The European Perspective
In contrast, European aviation has been shaped by its own unique challenges, including a denser airspace and shorter travel distances between countries. European manufacturers like Airbus have prioritized innovation and efficiency, often leading the way in implementing cutting-edge technology and environmentally friendly designs.
Design and Technology Differences

A key difference between American and European airplanes lies in their design philosophies and technological features. These differences are evident in various aspects, from cockpit layout to materials used in construction.
Cockpit Layout
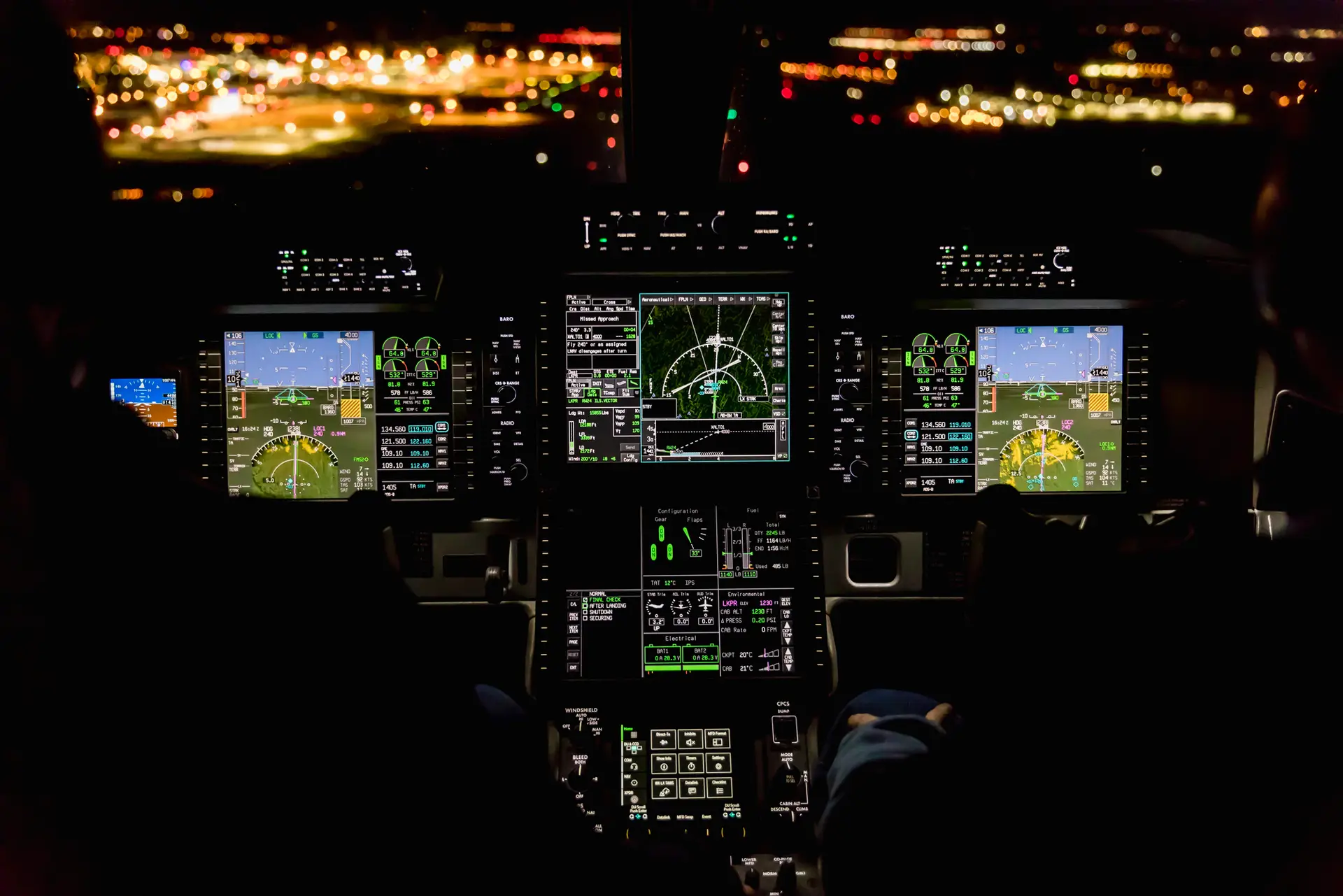
One of the most noticeable differences for commercial pilots is the cockpit design. American airplanes often feature a more traditional control layout, with a focus on manual controls and gauges. This design reflects a philosophy of giving pilots more direct control over the aircraft.
European airplanes, on the other hand, tend to have more advanced, computerized cockpits. Airbus, for example, is known for its fly-by-wire systems, which replace manual controls with electronic signals. This allows for more automation and can reduce pilot workload, although it requires a different set of skills and training.
Material Usage
The materials used in aircraft construction also differ between the two regions. American manufacturers have traditionally used aluminum as the primary material, valued for its strength and light weight. However, European companies have been quicker to adopt composite materials, which can offer even greater weight savings and improved fuel efficiency.
Safety and Regulations
Safety is paramount in aviation, and both American and European airplanes adhere to strict regulations. However, there are differences in how these regulations are implemented and enforced.
Regulatory Bodies
In the United States, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) is responsible for regulating all aspects of civil aviation. The FAA has a reputation for being very stringent, which has influenced the design and operation of American airplanes.
In Europe, the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) sets the regulatory standards. While EASA’s standards are also rigorous, they can differ from the FAA’s in certain areas, leading to variations in aircraft design and operation.
Safety Features
Both American and European airplanes are equipped with numerous safety features, but the approach to safety can differ. For example, European aircraft manufacturers have been pioneers in the development of systems like Traffic Collision Avoidance Systems (TCAS) and advanced autopilot functions.
Environmental Considerations

by Jacob43 (https://unsplash.com/@jacob43)
As environmental concerns become increasingly important, both American and European airplane manufacturers are focusing on sustainability. However, their approaches reflect their different priorities and regulatory environments.
Fuel Efficiency
European manufacturers have been at the forefront of developing fuel-efficient airplanes. Airbus, for example, has invested heavily in research to reduce fuel consumption and emissions. This focus is partly driven by European Union regulations, which impose stringent environmental standards.
American manufacturers have also made strides in improving fuel efficiency, but their approach often emphasizes balancing performance with cost-effectiveness. Boeing’s development of the 787 Dreamliner, with its composite materials and advanced engines, is a testament to this dual focus.
Noise Reduction
Noise pollution is another area where European and American airplanes differ. European manufacturers have been particularly proactive in developing quieter engines and technologies to minimize noise impact on communities near airports.
Cultural Influences
Cultural factors also play a role in shaping the differences between American and European airplanes. These influences can be seen in everything from design aesthetics to passenger comfort.
Aesthetic Preferences
American airplanes often have a more utilitarian design, focusing on functionality and durability. This reflects a broader cultural value placed on practicality.
European airplanes, meanwhile, might prioritize sleek, modern designs and passenger comfort. This is not only a reflection of cultural preferences but also a competitive strategy in the highly competitive European market.
Passenger Experience
The passenger experience can also vary between American and European airlines. European airlines often emphasize customer service and amenities, offering features such as more spacious seating and enhanced in-flight entertainment options.
In contrast, American airlines might prioritize operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness, which can result in a more straightforward passenger experience.
Conclusion
The differences between American and European airplanes are a fascinating reflection of each region’s unique history, priorities, and challenges. From design and technology to safety and environmental considerations, these distinctions have shaped the global aviation industry in profound ways.
Understanding these differences not only enhances appreciation for the complexity of modern aviation but also highlights the diverse approaches that can coexist in a globalized world.
Whether you’re a commercial pilot navigating these aircraft or a passenger experiencing them firsthand, the variations between American and European airplanes offer an intriguing glimpse into the world of aviation.



